
Intel’s anticipated successor to the low-power “Alder Lake-N” series appears to be the Wildcat Lake lineup, as revealed in newly uncovered shipping manifests. This series aims to continue Intel’s focus on power-efficient devices like mini-PCs, leveraging new technologies for enhanced efficiency.
Wildcat Lake SoCs: Cougar Cove, LPE Darkmont, and Intel’s 18A Node
The “Wildcat Lake” series is expected to debut alongside Intel’s “Panther Lake-H” lineup, marking another step forward in mobile computing. According to details shared by @x86deadandback, Intel’s Wildcat Lake SoCs are being developed as ultra-low-power solutions, set to replace the Alder Lake-N lineup.
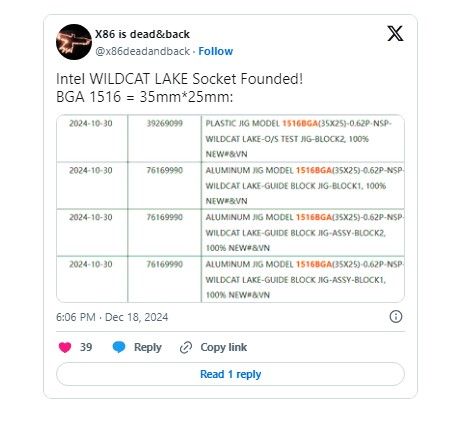
The shipping manifests indicate that Wildcat Lake chips will use a BGA 1516 socket type, measuring 35 x 25 mm. This socket differs from the mainstream LGA socket, employing a soldered design more suitable for compact, power-efficient devices. Interestingly, the manifests also mention CPU reballing equipment, suggesting the lineup is still in its early verification phase.
Speculation on Architecture and Configuration
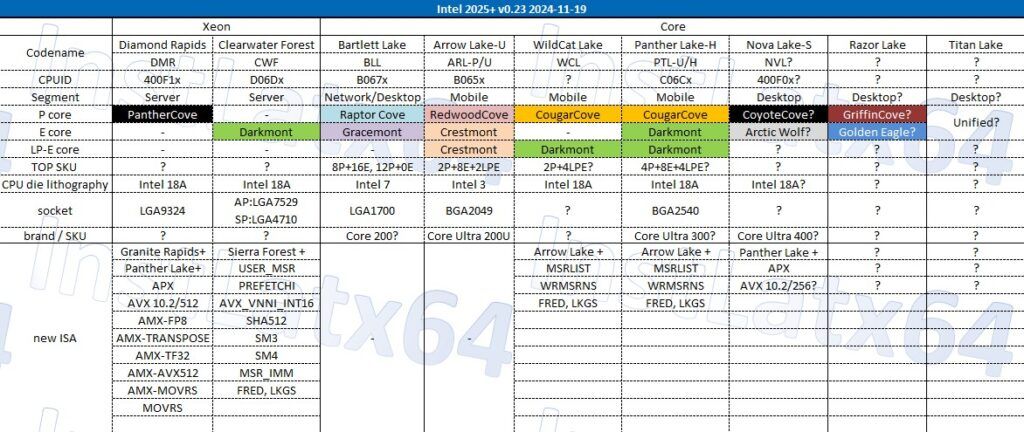
While specific details about Wildcat Lake remain sparse, rumors suggest it will feature Cougar Cove P-Cores and LPE Darkmont E-Cores in a 2+4 configuration. This hybrid architecture is designed to balance power efficiency with sufficient performance for lightweight tasks.
Additionally, this series is expected to introduce Intel’s 18A node, showcasing advanced fabrication technology. This marks a significant milestone for Intel Foundry, as the 18A node plays a pivotal role in Intel’s efforts to adopt cutting-edge manufacturing techniques.
Low-Powered Devices with High Efficiency
Wildcat Lake is targeted primarily at low-powered devices such as laptops and mini-PCs, much like its predecessor, Alder Lake-N. While peak performance may not be the lineup’s strong suit, its low TDP (Thermal Design Power) will ensure maximum efficiency. This focus on efficiency will likely extend to graphical performance, making these chips ideal for compact, portable systems that prioritize battery life and minimal power consumption.
Key Takeaways
Intel’s Wildcat Lake lineup reflects the company’s continued commitment to innovation in the low-power computing segment. By incorporating the 18A node, Cougar Cove cores, and a new BGA socket design, Intel aims to deliver efficient and reliable solutions for modern mobile devices.
Stay tuned for further updates on specifications, release timelines, and the broader implications of Wildcat Lake in Intel’s product lineup.





By Radoslav Jokic
Updated on 9th March 2025