
Overview of APT28’s Cyber Operations
APT28, also known as Fancy Bear and Forest Blizzard, is a notorious Russian state-sponsored hacking group linked to the Russian military intelligence agency GRU, specifically Unit 26165. This group has been active for over a decade and is primarily involved in cyber espionage activities aimed at collecting intelligence to support the Russian government’s foreign policy and military interests. The group has targeted a wide range of sectors across North America, Western Europe, and Ukraine, including governmental, non-governmental organizations, education, and transportation.
Exploitation of the Windows Print Spooler Vulnerability
APT28 has recently been in the spotlight for its exploitation of a significant vulnerability in the Windows Print Spooler service, tracked as CVE-2022-38028. This flaw, which involves privilege escalation within Windows systems, allows attackers to execute malicious code with SYSTEM-level permissions. Discovered and reported by the NSA, this vulnerability was patched by Microsoft in October 2022. However, it is believed that APT28 had been exploiting this vulnerability since at least June 2020, and possibly as early as April 2019.
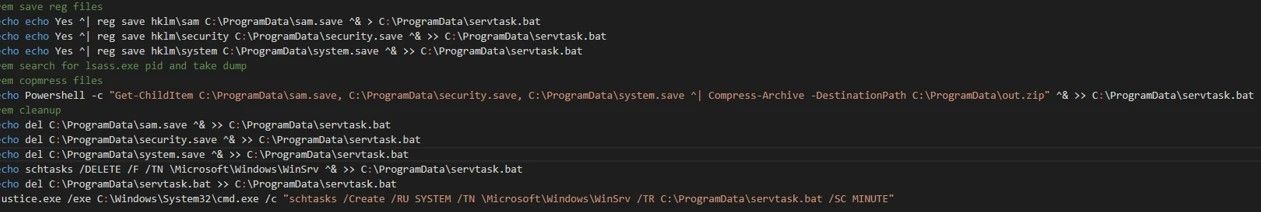
GooseEgg Malware Deployment
The deployment of the GooseEgg malware by APT28 is particularly concerning due to its capabilities and stealth. GooseEgg is a custom-developed tool used by the group to exploit the CVE-2022-38028 vulnerability effectively. It is a simple yet powerful launcher application that can initiate other applications with elevated permissions. This functionality allows APT28 to perform a range of follow-on activities, such as installing backdoors, moving laterally through networks, and executing additional malicious payloads.
Technical Insights into GooseEgg
GooseEgg is typically delivered through a batch script, which modifies a JavaScript constraints file to trigger the exploitation of the Windows Print Spooler service. Once executed, it allows APT28 to maintain persistent access to compromised systems. The malware supports commands to launch either a provided dynamic-link library (DLL) or an executable with elevated permissions, facilitating further exploitation and control over the infected systems.

Broader Implications and APT28’s Recent Activities
The activities of APT28 are part of a broader pattern of Russian cyber operations that focus on intelligence gathering and disruption. In addition to exploiting CVE-2022-38028, APT28 has also been reported to utilize other significant vulnerabilities, such as a privilege escalation flaw in Microsoft Outlook (CVE-2023-23397) and a code execution bug in WinRAR (CVE-2023-38831). These activities highlight the group’s adaptability and the sophisticated nature of its operations, which often leverage publicly available exploits to enhance their capabilities.
Security Recommendations
To defend against threats posed by APT28 and similar state-sponsored actors, organizations
are advised to implement several critical security measures:
- Timely Patch Management: Organizations must prioritize timely updates and patches, particularly for disclosed vulnerabilities that are known to be exploited in the wild. The prompt application of patches for vulnerabilities like CVE-2022-38028 is essential to prevent exploitation by actors like APT28.
- Disable Non-Essential Services: In environments where security is a high priority, such as domain controllers, services like the Print Spooler, which have historically been targeted for vulnerabilities, should be disabled if they are not necessary for daily operations.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): Running EDR tools in block mode can help detect and block malicious activity derived from malware execution attempts before they can cause significant harm.
- Advanced Monitoring and Logging: Implementing comprehensive logging and monitoring solutions can help detect unusual activities and potential breaches. It’s crucial to monitor common attack vectors and maintain logs for all critical system activities to facilitate timely detection and response.
- User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA): Utilizing UEBA can help in identifying deviations from normal user behaviors, which could indicate compromised accounts or insider threats.
- Incident Response Planning: Organizations should have an updated incident response plan that includes procedures for dealing with ransomware attacks and breaches involving critical infrastructure. Regular drills or simulations of cyberattacks should be conducted to ensure the readiness of the response team.
- Security Awareness Training: Regular training sessions for employees can significantly reduce the risk of successful phishing attacks, which are often the initial entry point for more severe attacks. Educating employees about the latest phishing tactics and encouraging them to report suspicious emails can create a proactive security culture.
- Network Segmentation: By segmenting networks, organizations can limit the lateral movement of APT28 or other attackers, confining the damage to isolated parts of the network. Proper segmentation involves strict controls on traffic flow between network segments, potentially preventing the spread of malware.
- Multi-factor Authentication (MFA): Implementing MFA can add an additional layer of security, making it more difficult for attackers to gain unauthorized access even if they have compromised credentials.

(Image creidt: arstechnica)
Conclusion
The activities of APT28, particularly its exploitation of the CVE-2022-38028 vulnerability through tools like GooseEgg, highlight the sophisticated and continually evolving nature of state-sponsored cyber threats. These actors adapt quickly to exploit new vulnerabilities and are persistent in their efforts to achieve their objectives. Organizations must remain vigilant, applying a layered security approach that includes both technological solutions and human factors to defend against these advanced threats effectively.







By Andrej Kovacevic
Updated on 14th July 2024